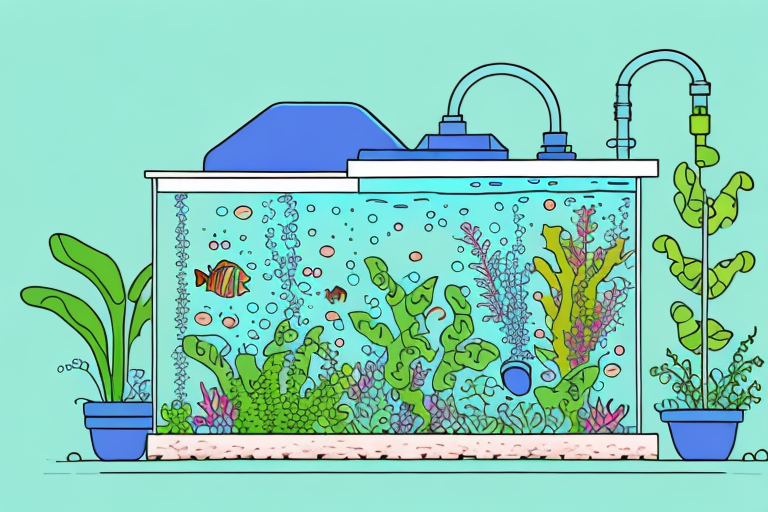
Aquaponics is an innovative and sustainable method of gardening that combines aquaculture (the cultivation of fish) and hydroponics (the growing of plants without soil). Through a symbiotic relationship between fish and plants, aquaponic systems create a self-contained ecosystem where both elements thrive. This article aims to provide a comprehensive step-by-step guide to help beginners understand the intricacies of aquaponics and set up their own successful aquaponic garden.
What is Aquaponics and How Does it Work?
Aquaponics is a closed-loop system that harnesses the natural relationship between fish and plants. The fish produce waste, which contains ammonia, a toxic substance for them if not removed. However, this waste can be beneficial for plants. In an aquaponic system, the water containing fish waste is pumped into grow beds where bacteria convert the ammonia into nitrites and then into nitrates. These nitrates serve as a nutrient-rich fertilizer for the plants. The plants, in turn, absorb the nitrates, purifying the water before it is returned to the fish tank. This cycle continues, creating a sustainable and highly efficient method of growing both fish and plants.
Understanding the Benefits of Aquaponics
Aquaponics offers numerous benefits compared to traditional gardening methods. Firstly, it requires significantly less water as the same water is recycled throughout the system. Secondly, it eliminates the need for chemical fertilizers as the fish waste provides the necessary nutrients for plant growth. Additionally, aquaponics can produce a higher yield of fruits, vegetables, and herbs since the plants receive a constant supply of nutrients. Furthermore, this sustainable method allows for year-round gardening, regardless of climate or season. Finally, aquaponics promotes biodiversity as it creates a harmonious environment for both fish and plants to thrive.
The Basic Components of an Aquaponics System
An aquaponic system consists of several essential components. Firstly, there is the fish tank, which provides a habitat for the aquatic animals. The water from the fish tank is pumped into the grow beds, where the plants are grown. These grow beds can be filled with a medium such as gravel or expanded clay pellets. The water then flows back to the fish tank after being filtered and purified by the plants. A water pump, air pump, and plumbing system are necessary to maintain proper water circulation and aeration. Additionally, the system may include a sump tank, which helps regulate water levels and provides additional space for beneficial bacteria to thrive.
Choosing the Right Fish for Your Aquaponics System
The choice of fish for your aquaponics system is crucial as they are the primary source of nutrients for the plants. Ideally, you should select fish that can tolerate a wide range of water conditions and are well-suited for closed-system environments. Tilapia, trout, catfish, and koi are popular choices due to their resilience and adaptability. However, it is essential to consider factors such as water temperature, pH levels, and dietary requirements when selecting fish species for your aquaponic garden. Additionally, local regulations and restrictions may influence your choice of fish.
Selecting the Ideal Plants for Aquaponics
When choosing plants for your aquaponic system, it is important to consider their compatibility with the nutrient-rich water and the specific conditions of your setup. Leafy greens such as lettuce, kale, and spinach are excellent choices as they thrive in nutrient-rich environments. Herbs like mint, basil, and parsley are also well-suited for aquaponics. Additionally, tomatoes, cucumbers, and peppers can be successfully grown in larger systems. It is recommended to start with a variety of plants to observe their performance and adaptability to your specific aquaponics setup.
Setting Up Your Aquaponics System: A Detailed Guide
Setting up an aquaponic system may seem daunting, but with careful planning and attention to detail, beginners can achieve success. The first step is to determine the location for your system, considering factors such as sunlight exposure, temperature fluctuations, and proximity to electricity and water sources. Once the location is selected, you can start assembling the components of your aquaponics system, including the fish tank, grow beds, plumbing, and pumps. Proper seed selection and germination techniques are crucial for successful plant growth. Finally, you need to establish the nitrogen cycle by introducing fish slowly and allowing the necessary bacteria to colonize the system. Regular monitoring and maintenance are essential to ensure the health and productivity of your aquaponic garden.
Essential Tools and Equipment for Aquaponics
Having the right tools and equipment is vital for the efficient operation and maintenance of your aquaponics system. Some essential items include a water pump to circulate the water, an air pump for oxygenation, grow bed media, grow lights (if growing indoors), pH test kits, thermometers, and fish nets. It is also beneficial to have a backup power source, such as a battery-powered air pump, in case of power outages. Additionally, a water testing kit and a nutrient solution may be required to maintain optimal water quality and nutrient levels in the system.
The Best Location for Your Aquaponics System
The location of your aquaponics system plays a crucial role in its success. Ideally, the system should be placed in an area with ample sunlight, as most plants require at least six hours of direct sunlight daily. If you plan to set up an indoor aquaponic garden, grow lights can supplement natural sunlight. It is important to choose a level and stable surface that can support the weight of the system. Additionally, consider factors such as temperature fluctuations, accessibility for maintenance, and proximity to a water source and electrical outlets when selecting the location for your aquaponics setup.
Water Quality Management in Aquaponics: Tips and Tricks
Maintaining optimal water quality is essential for the health and productivity of both fish and plants in an aquaponic system. Regular monitoring of pH levels, temperature, dissolved oxygen, and ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels is crucial. The pH level should be maintained within a specific range (typically 6.8-7.2) to ensure nutrient availability for plants and the well-being of fish. Adequate filtration, aeration, and circulation are necessary to prevent the buildup of harmful substances. Introducing beneficial bacteria and periodically checking water quality parameters will help you keep your aquaponic system in balance.
Feeding and Caring for Fish in an Aquaponics System
The proper care and feeding of fish are crucial for their health and growth in an aquaponic system. It is important to select a high-quality fish feed that meets the nutritional requirements of the chosen species. Overfeeding should be avoided, as it can lead to excess waste and water quality issues. Regular monitoring of fish behavior and appearance is essential to detect any signs of disease or stress. Additionally, providing suitable shelter and minimizing stressors such as sudden temperature fluctuations or aggressive tankmates will contribute to the overall well-being of the fish in your aquaponic garden.
Maintaining Proper pH Levels in Your Aquaponics System
The pH level affects the availability of nutrients to plants and the overall health of fish in an aquaponic system. Monitoring and maintaining the pH should be a regular part of system maintenance. Various factors can influence pH, including water source characteristics, fish waste, plant uptake of minerals, and the presence of nitrifying bacteria. If the pH drifts outside the recommended range, adjustments can be made using pH-up or pH-down solutions specifically formulated for aquaponics. Care should be taken to avoid sudden and drastic changes in pH levels, as they can stress or harm the fish and plants.
Understanding Nitrogen Cycling in Aquaponics
The nitrogen cycle is a crucial process in aquaponics that converts toxic ammonia excreted by fish into nitrites and eventually into nitrates, which are beneficial for plants. Beneficial bacteria play a vital role in this process. It is essential to establish the cycle before introducing fish to the system. During the initial cycling period, ammonia levels will spike, followed by nitrite levels. Regular testing and monitoring of ammonia and nitrite levels will help determine when the system is ready for fish. Patience and careful observation are key to ensuring a healthy and stable nitrogen cycle within your aquaponic system.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in Aquaponics Systems
While aquaponics offers many benefits, it is not without its challenges. Various problems may arise during the operation of an aquaponic system. These can include water quality issues, nutrient deficiencies in plants, fish diseases, or pests. Regular monitoring, frequent water testing, and visual inspection of both fish and plants will help detect and address potential problems before they escalate. Proper research, understanding, and experience will equip you to troubleshoot and resolve common issues, ensuring the long-term success of your aquaponic garden.
Maximizing Crop Production in Your Aquaponics Garden
To maximize crop production in your aquaponics garden, several factors should be considered. Choosing the appropriate plant varieties that are well-suited to your system and environmental conditions is essential. Implementing proper plant spacing and trellising techniques will optimize sunlight penetration and airflow, promoting healthy growth. Regular pruning and harvesting techniques will enhance productivity and encourage new growth. Additionally, maintaining adequate nutrient levels and addressing any nutrient deficiencies promptly will contribute to the overall health and productivity of your plants in the aquaponic system.
Harvesting and Using the Produce from Your Aquaponics System
Harvesting the produce from your aquaponics system is an exciting and rewarding experience. Depending on the plants you’ve grown in your system, harvesting methods and timing may vary. Leafy greens can be harvested by carefully removing individual leaves, while fruits and vegetables are typically picked when fully ripe. Ensure proper sanitation and cleanliness when harvesting to prevent contamination. Freshly harvested produce from your aquaponics system can be used in various culinary creations, providing a satisfying taste of the fruits of your aquatic and horticultural endeavors.
Expanding Your Aquaponics Setup: Scaling Up and Adding New Features
Once you have gained confidence and success with your initial aquaponic setup, you may consider expanding your system. Scaling up can involve adding additional grow beds, increasing the size of the fish tank, or incorporating new features such as a larger sump tank or a greenhouse. It is important to plan and design the expansion carefully, ensuring the balance and functionality of the system are maintained. Taking gradual steps and monitoring the impact of each change will help ensure a smooth transition and continued success with your expanded aquaponics setup.
Exploring Different Types of Aquaponic Systems: NFT, DWC, and Media Beds
Aquaponic systems can be designed in various ways, each utilizing different methods for delivering water and nutrients to the plants. Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) systems use a shallow stream of water flowing over the plant roots to provide nutrients. Deep Water Culture (DWC) systems immerse the plant roots directly in the water, allowing them to absorb nutrients. Media Bed systems, the most common type, use a medium such as gravel or expanded clay pellets to support plant growth and provide space for beneficial bacteria to grow. Each system has its advantages and considerations, allowing aquaponics enthusiasts to choose the approach that best suits their needs and preferences.
A Comparison of Organic vs Conventional Methods in Aquaponics
Aquaponics offers a sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to gardening, aligning with organic principles. By eliminating the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, aquaponics provides an organic method of growing fresh and healthy produce. The closed-loop system reduces water consumption and eliminates runoff, minimizing the impact on the environment. The absence of soil in aquaponics eliminates the risk of soil-borne diseases and pests, promoting cleaner and safer food production. While aquaponics can be considered organic, it is important to source organic fish feed and ensure the overall inputs in the system meet organic standards.
Tips for a Successful DIY Aquaponics Project
Undertaking a DIY aquaponics project can be an exciting and fulfilling endeavor. To ensure success, it is essential to plan carefully and consider the specific requirements of your setup. Thorough research and understanding of aquaponics principles are crucial before starting. Start with a small-scale system to gain experience and confidence before scaling up. Regular monitoring and maintenance, combined with attention to water quality, will contribute to the success of your project. Seek guidance from experienced aquaponics enthusiasts and be open to learning from both successes and challenges. With patience, perseverance, and a passion for sustainable gardening, your DIY aquaponics project can flourish.
Implementing aquaponics as a gardening method offers a unique and sustainable approach to cultivating both fish and plants. With the comprehensive step-by-step guide provided in this article, beginners can confidently dive into the world of aquaponics and embark on a rewarding journey of self-sufficiency and environmental stewardship. By understanding the principles, components, and care required for aquaponics systems, you can create a thriving ecosystem that not only produces nutritious food but also fosters a deeper connection with nature and the fascinating interplay between aquatic life and plant growth.