Aquaponics is a sustainable farming solution that has gained significant attention in recent years. The integration of aquaculture and hydroponics in this innovative technique has revolutionized the agriculture sector. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of aquaponics, including its working mechanism, growing popularity, and its environmental and economic impacts. Additionally, we will delve into inspiring success stories from the aquaponics industry, highlighting case studies that demonstrate the potential of this farming method. Join us as we uncover the transformative power of aquaponics and its promising future.
Introduction to Aquaponics: A Sustainable Farming Solution
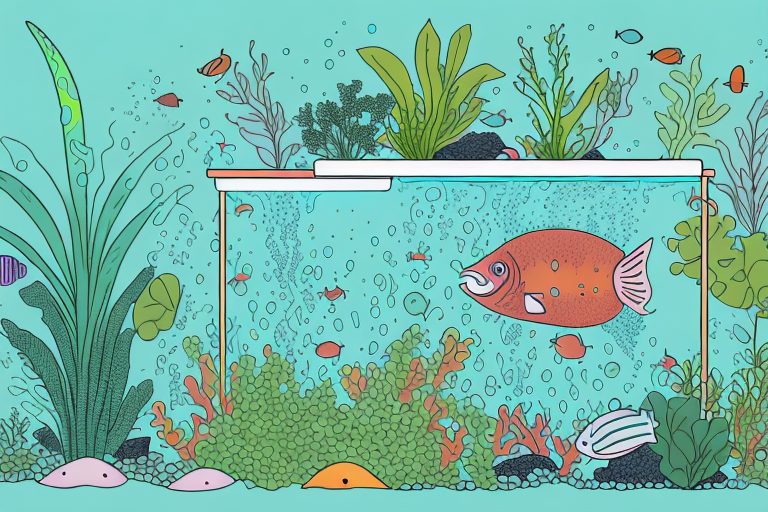
Aquaponics is a closed-loop farming system that combines aquaculture, the cultivation of aquatic animals, with hydroponics, the cultivation of plants in water. In this symbiotic system, fish waste provides nutrients for plant growth, while the plants filter and purify the water for the fish. This efficient collaboration between fish and plants creates a self-sustaining ecosystem that requires minimal external inputs.
One of the key benefits of aquaponics is its ability to conserve water. Compared to traditional soil-based farming, aquaponics uses up to 90% less water. This is because the water in the system is continuously recirculated and reused, rather than being lost through evaporation or runoff. Additionally, the plants in an aquaponics system require less water than those grown in soil, as they can directly access the nutrients dissolved in the water.
Another advantage of aquaponics is its potential for year-round production. By controlling the environment in which the system operates, such as temperature and lighting, farmers can create optimal conditions for plant growth regardless of the season. This allows for a consistent and reliable harvest, reducing the dependence on external factors such as weather patterns. Furthermore, the controlled environment also minimizes the risk of pests and diseases, leading to healthier and more productive crops.
How Aquaponics Works: The Integration of Aquaculture and Hydroponics
In an aquaponic system, the fish are housed in tanks or ponds, and their waste releases ammonia into the water. Beneficial bacteria convert the harmful ammonia into nitrates, which serve as nutrients for the plants. The plants, usually leafy greens or herbs, are grown in grow beds or vertical towers that are continuously flooded with the nutrient-rich water.
The plants absorb the nitrates, effectively removing them from the water. This purified water is then recirculated back to the fish tanks or ponds, ensuring a continuous flow of nutrients for both the fish and the plants. This cycle allows for a highly efficient use of resources, as water is conserved and nutrients are recycled.
Aquaponics offers several advantages over traditional farming methods. One major benefit is the reduction in water usage. Compared to conventional agriculture, aquaponics uses up to 90% less water. This is because the water in the system is continuously recycled, with only minimal amounts lost through evaporation or plant transpiration.
Another advantage of aquaponics is its ability to produce both fish and plants simultaneously. This integrated approach allows for a diverse range of crops to be grown, providing a more sustainable and balanced food production system. Additionally, the fish in the system can be harvested for consumption, providing a source of protein alongside the plant crops.
The Growing Popularity of Aquaponics in the Agriculture Sector
Aquaponics has gained significant popularity in the agriculture sector due to its numerous benefits. Firstly, it offers a sustainable alternative to traditional farming methods by conserving water and minimizing the need for synthetic fertilizers. Additionally, aquaponics systems can be set up in both rural and urban areas, making it accessible to a wide range of farmers.
Furthermore, aquaponics allows for year-round cultivation, as it is not dependent on seasonal variations. This flexibility provides farmers with a consistent supply of fresh produce, helping meet the growing demands of consumers for locally sourced, pesticide-free food.
Moreover, aquaponics promotes biodiversity and ecological balance. The symbiotic relationship between fish and plants in an aquaponics system creates a self-sustaining ecosystem. The fish waste provides nutrients for the plants, while the plants filter the water, creating a clean and healthy environment for the fish. This natural cycle reduces the need for chemical pesticides and herbicides, resulting in a more environmentally friendly farming method.
Case Study 1: Transforming a Small-Scale Farm into a Profitable Aquaponics Operation
One success story in the aquaponics industry is the transformation of a small-scale farm into a profitable operation. In this case, a farmer in a rural community faced challenges in traditional farming due to limited resources and unfavorable growing conditions.
By adopting aquaponics, the farmer was able to overcome these obstacles and significantly increase productivity. The integration of fish and plants not only provided a diversified income stream but also allowed for the cultivation of high-value crops that were in demand in the local market.
Through careful planning and continuous learning, the farmer optimized the system to maximize efficiency and minimize waste. By diversifying the crops and continuously experimenting with new varieties, the farm became a thriving example of how aquaponics can revitalize small-scale farming operations.
Furthermore, the farmer implemented sustainable practices in the aquaponics system, such as using organic feed for the fish and avoiding the use of chemical pesticides and fertilizers. This not only ensured the production of healthy and environmentally-friendly crops but also appealed to consumers who prioritize sustainable and organic products.

2 thoughts on “Case Study: Success Stories in the Aquaponics Industry”
Comments are closed.