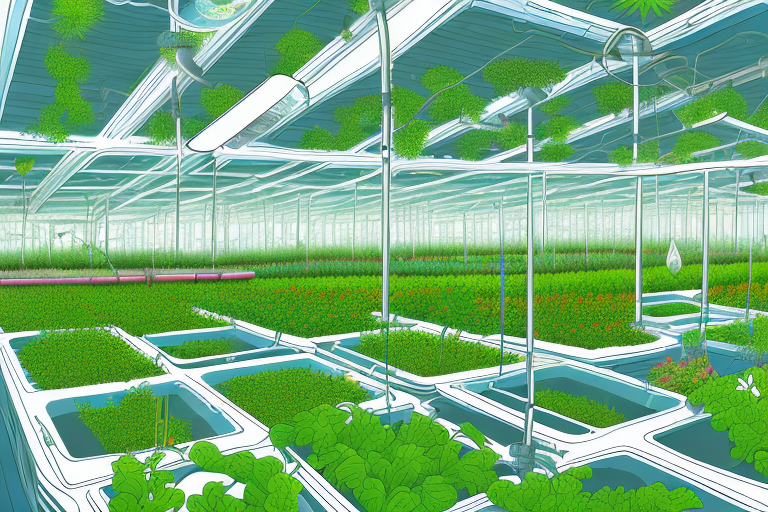
Aquaponics farming offers a sustainable and efficient way to grow both fish and plants together in a mutually beneficial system. As an aquaponics farmer, you may have already experienced the advantages of this method in terms of reduced water usage, improved nutrient cycling, and overall productivity. However, if you are looking to further enhance your farm’s output and space efficiency, it is worth considering other innovative techniques, such as vertical farming.
Understanding the concept of vertical farming and its benefits in aquaponics
Vertical farming is a unique approach to agriculture that involves growing plants in vertically stacked layers, often in controlled environments such as greenhouses or hydroponic systems. This technique maximizes the use of available space, allowing farmers to produce significantly higher yields compared to traditional farming methods.
In the context of aquaponics, vertical farming offers several benefits. Firstly, it allows you to maximize production in a limited space. By utilizing vertical structures and tiered growing systems, you can grow more plants in the same area, effectively increasing your yield without expanding your farm’s footprint. Furthermore, vertical farming enables you to create optimal growing conditions for various crops, regardless of external environmental factors. This is particularly advantageous for aquaponics, as the plants and fish require specific temperature, light, and nutrient conditions to thrive.
Another advantage of vertical farming in aquaponics is the efficient use of water. In traditional farming, a significant amount of water is lost through evaporation and runoff. However, in vertical farming systems, water is recirculated and reused, minimizing water waste. This is especially important in aquaponics, where water is a vital component for both plant growth and fish health.
Additionally, vertical farming in aquaponics can help reduce the reliance on pesticides and herbicides. By growing plants in a controlled environment, the need for chemical interventions to combat pests and weeds is significantly reduced. This not only benefits the environment by minimizing chemical runoff but also promotes healthier and more sustainable food production.
Exploring the advantages and disadvantages of vertical farming in aquaponics
Like any farming technique, vertical farming in aquaponics has its pros and cons that need to be considered before implementation.
On the plus side, vertical farming allows for higher crop density, which means maximizing production per square foot of space. This can be particularly beneficial in urban settings or areas where available land is limited. Additionally, the controlled environment in vertical farms reduces the risk of pests and diseases, resulting in healthier and more resilient plants. Moreover, since vertical farming typically involves hydroponics or aeroponics, it eliminates the need for soil, making it a viable solution for areas with poor soil quality.
However, vertical farming also comes with some challenges. The initial setup cost can be higher compared to traditional aquaponics systems, as additional infrastructure, such as grow lights, ventilation systems, and automated controls, may be required. Additionally, the energy consumption of vertical farms should not be overlooked, as maintaining the ideal conditions for plant growth might require significant electricity usage. It is important to carefully evaluate these factors and calculate the potential return on investment before deciding to adopt vertical farming in your aquaponics farm.
Another disadvantage of vertical farming in aquaponics is the potential for system failures. Vertical farms rely heavily on technology and automation, which means that any malfunction or power outage can disrupt the entire system. This can lead to crop loss and financial setbacks for farmers. It is crucial to have backup systems in place and regularly maintain and monitor the equipment to minimize the risk of system failures.
How vertical farming can help maximize production and space efficiency in your aquaponics farm
Vertical farming offers numerous strategies to optimize production and space efficiency in aquaponics farms.
One of the key advantages of vertical farming is the ability to utilize vertical space effectively. By implementing tiered growing systems, you can take advantage of vertical layers, allowing for a much higher plant density than in traditional farming methods. This effectively multiplies the available growing area, maximizing your farm’s production potential.
Furthermore, vertical farming provides precise control over environmental conditions. By using smart technologies and data analytics, you can ensure that plants receive the ideal amounts of light, water, and nutrients, resulting in faster growth and higher yields. Sensors can monitor temperature, humidity, and nutrient levels, allowing for real-time adjustments to optimize plant growth and promote a healthy aquaponics system.
In addition to vertical farming, there are other innovative techniques that can help maximize production and space efficiency in aquaponics farms. These include utilizing floating raft systems, which allow plants to grow on the water’s surface, effectively utilizing both horizontal and vertical space. Additionally, incorporating rotating or movable grow beds can maximize sunlight exposure by moving plants throughout the day, ensuring uniform growth and reducing shading effects. These techniques, when combined with vertical farming, can further enhance your farm’s productivity.
Another technique that can be employed to maximize production and space efficiency in aquaponics farms is the use of vertical stacking. This involves stacking multiple layers of growing beds vertically, similar to a shelving system. By utilizing this method, you can significantly increase the number of plants that can be grown in a limited space. Each layer can be dedicated to different types of plants, allowing for a diverse range of crops to be cultivated simultaneously. Vertical stacking also facilitates easy access to plants for maintenance and harvesting, as each layer can be individually accessed without disturbing the others. This technique is particularly beneficial for small-scale aquaponics farms or urban farming setups where space is limited.